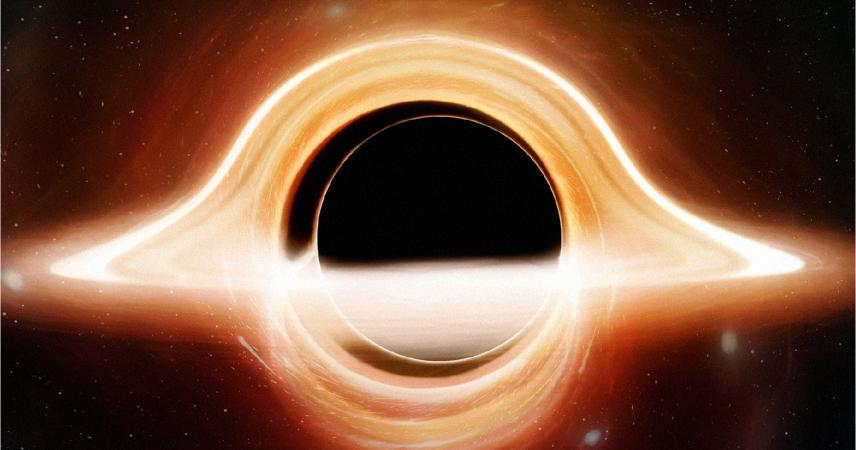
The spark of Einstein’s genius…
In 1915, Albert Einstein published his theory of general relativity, which completely changed our perspective of gravity.
Space and time are inseparable concepts, and gravity is simply the curvature of the fabric of space-time in the presence of matter.
And the greater and more compact that matter is, the greater the distortion of space around it.
To help us to to visualise this, let’s just imagine the orbits of the planets around the Sun: they are simply the fastest routes that can be taken by objects trapped in the curved space created by the presence of the Sun.
Stars In the star formation process, matter, primarily hydrogen atoms, contracts under its own weight, and the pressure at the core of the proto-star becomes so great that nuclear reactions are triggered. have various sizes. Our Sun is a medium-sized star, but there are massive stars that are much larger.
In the star formation process, matter, primarily hydrogen atoms, contracts under its own weight, and the pressure at the core of the proto-star becomes so great that nuclear reactions are triggered.
Like giant natural nuclear fusion power plants, stars produce energy by turning hydrogen into helium and then gradually into more complex elements. These nuclear reactions make the stars shine and enable them to generate the energy that they need so as not to collapse under their own weight.
However, stars have an expiration date. When the elements inside them are no longer able to generate nuclear reactions, stars begin to contract under their own weight. Their final fate will depend on their mass.
The largest and most massive stars, that are several times larger than the size of our Sun, collapse very quickly onto their core, and create a shockwave that makes their outer layers explode. We are witnessing an event known as a supernova explosion.
What remains of the core continues to contract. Nothing can stop its collapse, and all the matter ends up condensed in a very small dense region. To give ourselves an idea, the Earth would have to shrink to the size of a marble.
Space is so distorted that it becomes a bottomless pit. Nothing can escape, not even light… A black hole has been formed.
Any object that approaches, is torn apart and its elements start to fall into this bottomless pit and create a whirlpool .
The most common black holes are the inexorable end of the most massive stars. It is estimated that only in our galaxy, the Milky Way, there may be from tens of millions to thousands of millions of black holes.
However, there is also another type of black hole that we call supermassive, that can be found at the centre of galaxies. These objects can reach from a million to a billion times the mass of our Sun. These objects are found at the centre of galaxies. At the centre of the Milky Way there is a supermassive black hole that dominates the gravitational field of our galaxy, and can destroy entire stars.
More than a hundred years have gone by since Einstein formulated the Theory of Relativity. We now know that black holes exist and the most massive ones play an important role in galaxy evolution. What happens inside them is still a mystery that requires a new theory.
According to Vera Rubin, an astronomer who contributed to the discovery of dark matter: “Still more mysteries of the universe remain hidden... Their discovery awaits the adventurous scientists of the future".